What are the important points about gestational diabetes?
- Gestational diabetes is the increase in the blood sugar that usually occurs at a certain stage of pregnancy, commonly during the second half.
- There’s an unclear cause of gestational diabetes, only that when a pregnant woman becomes resistant to insulin that results in higher blood glucose level.
- Gestational diabetes may be diagnosed through a blood test or oral glucose challenge test (OGTT).
- Obesity, history of gestational diabetes from the previous pregnancy, and history of pre-diabetes are among the risk factors of gestational diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes may seem normal to others. However, for some with higher glucose level, this can affect the developing baby.
In the Philippines, a long list of drugstores offers not only medicines but also free consultation aiming to keep track of a person’s health. This is especially important for pregnant women given that they are sensitive. It is also best to monitor their pregnancy to avoid complications in the nearing labor.
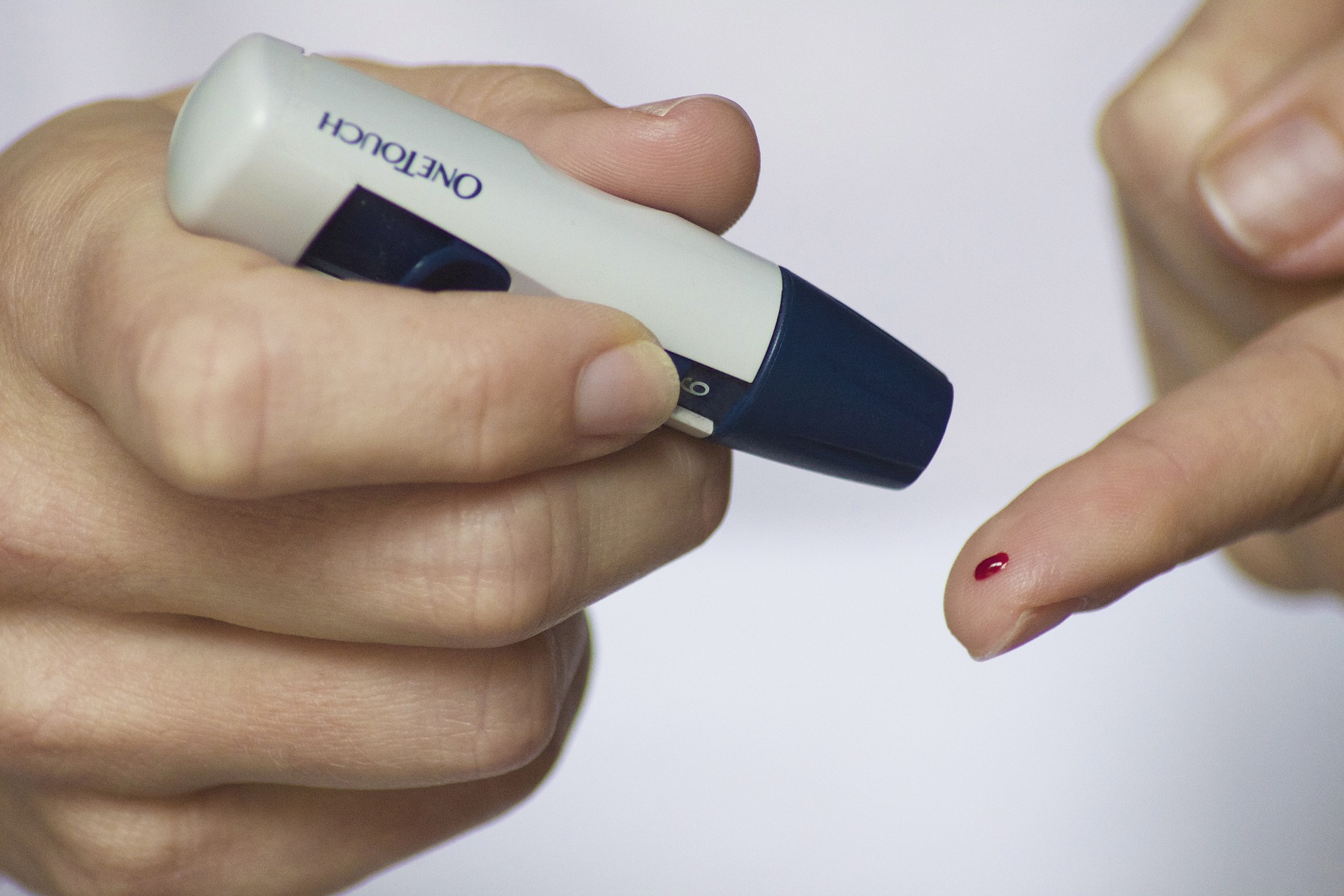
What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is the increase in blood sugar that usually occurs at a certain stage of pregnancy (commonly during the second half). At some cases, this also disappears after giving birth. As statistics conclude, about 4% of all pregnancies develop gestational diabetes.
What causes it?
It is still unclear as to why some women develop gestational diabetes, while others do not. Some experts theorize that this may be due to changes that occur during pregnancy. One factor, however, that is clear to them is women’s resistance to insulin. This resistance to insulin may result in a low level of insulin, causing the blood glucose levels to rise.
How is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
Often times, there are no symptoms that can show whether a gestational diabetes is already developing in a pregnant woman. Thus, screening tests are particularly significant.
Most likely, this is done through a blood test. The doctor may ask you to drink a sugar-rich beverage and then will draw blood from you typically an hour later. This is to examine the glucose for another hour later. Now, if the test result turns out as ‘not’ normal, the doctor may put you through another round of test to confirm the diagnosis.
Aside from the blood test, the doctor may also perform an oral glucose challenge test (OGTT), another type of test in screening glucose level. Through this test, your baseline blood glucose level will be checked, and then measured at around 1 to 3 hours after drinking a sugar-rich beverage.
What are the risk factors of gestational diabetes?
While some instances of insulin resistance may seem normal in the late stages of a woman’s pregnancy, there are others which may develop gestational diabetes. Some risk factors that may increase the risk of developing gestational diabetes to a pregnant woman may include:
- A history of gestational diabetes from a previous pregnancy
- Obesity
- A family member (commonly a parent or sibling) with type 2 diabetes
- An African American, Asian American, American Indian, Pacific Islander American, or Hispanic origin
- A history of pre-diabetes
- A history of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
How can gestational diabetes affect the development of the baby?
At most cases, women who are diagnosed with gestational diabetes receives proper health care as they go through the final stages of pregnancy and until delivery. However, for some who have high blood glucose levels during their pregnancy, this may cause the fetus to have high blood glucose levels as well. This can cause the fetus to be larger which can cause complications during the delivery. Some cases also showed that the baby may become overweight and develop type 2 diabetes as it grows.
Key Takeaway
Having an ample knowledge about gestational diabetes should definitely be given priority nowadays to pregnant women to ensure that they are safe and that the baby is healthy.
Hence, in our great aim to provide sufficient information regarding gestational diabetes, we’ll also discuss various ways to prevent developing this ailment in our next article.