Cardiovascular diseases: types, causes, symptoms, and medication
Cardiovascular disease is an umbrella term that can refer to a number of conditions related to the heart (cardio) or blood vessels (vascular). Cardiovascular diseases account for almost 20% of the deaths in the Philippines.
What is a cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease is a term used to refer to diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. These include:
- Heart disease
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Arrythmia
- Heart valve problems
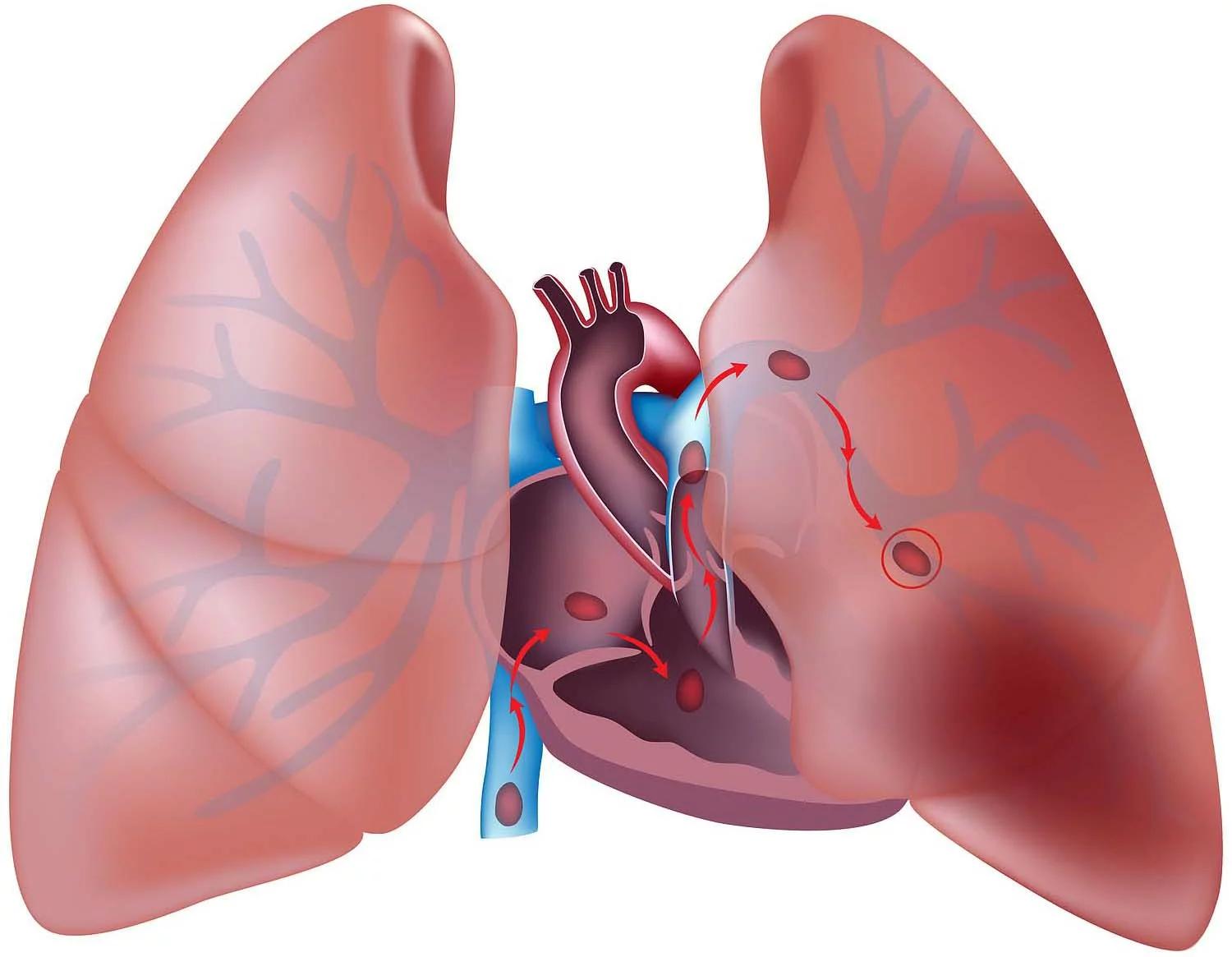
Cardiovascular diseases are typically associated with a buildup of fatty deposits inside the arteries and an increased risk of blood clots.
It can also refer to damage to the arteries in organs like the brain, heart, kidneys, and eyes.
What are the causes of a cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular diseases are caused by a buildup of fatty deposits (atheroma) that end up blocking the walls of the arteries around the heart. The buildup of atheroma makes the arteries narrower, making it more difficult for blood to flow to the heart. This is called atherosclerosis.
You have a higher risk of developing atherosclerosis if you:
- Smoke
- Have high blood pressure (hypertension)
- Have high cholesterol
- Have high levels of lipoprotein (a)
- Do not exercise regularly
- Are overweight or obese
- Have a history of cardiovascular diseases in the family
What are the symptoms of a cardiovascular disease?
The most common signs and symptoms of a cardiovascular disease are chest pain (angina) and breathlessness. Not all people will experience these symptoms before being diagnosed. Some people with cardiovascular disease may not feel any symptoms at all.
What are the drugs used to treat cardiovascular disease?
There are many different drugs used to treat cardiovascular disease. They are mainly used to reduce blood pressure or to widen the arteries, making it easier for blood to flow in and out of the heart.
Most medications will need to be used for life. Do not stop taking them without first consulting your doctor. If you stop taking your medications abruptly, you may make your symptoms worse.
Some generic drugs for cardiovascular diseases include:
- Blood-thinning medicines – reduce the risk of a heart attack by thinning your blood which prevents it from clotting
- Low-dose aspirin
- Clopidogrel
- Rivaroxaban
- Ticagrelor
- Prasugrel
- Statins – used to lower high cholesterol levels
- Atorvastatin
- Simvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Pravastatin
- Beta blockers – prevents angina and treats high blood pressure
- Atenolol
- Bisoprolol
- Metoprolol
- Nebivolol
- Nitrates or vasodilators – widens blood vessels
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors – treats high blood pressure
- Ramipril
- Lisinopril
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) – block the action of angiotensin.
- Valsartan
- Losartan
Related Blogs
-
January 4, 2021
Diabetes, Press, Healthy Lifestyle
4 Diseases You Can Develop Because Of Obesity
What are the diseases you can develop because of obesity? Type 2 Diabetes Heart Diseases Osteoarthritis Sleep Apnea Having [...]
-
January 28, 2021
Trending
5 Causes Of Chest Pain
What are the causes of chest pain? Heart attack Heart problems Gastrointestinal conditions Lung diseases Muscle, bone, and tissue [...]
-
June 26, 2020
Healthy Lifestyle
5 Effective Tips For Healthy Lungs
What are effective tips for healthy lungs? Stop smoking Get vaccinated Maintain an active lifestyle Avoid pollutants Eating [...]
-
January 5, 2021
Hypertension
Ang Mga Sanhi ng Atake Sa Puso
Ano ang mga sanhi ng atake sa puso? Coronary Artery Disease Coronary Spasm Vices COVID-19 Infection Ang heart attack o [...]
-
May 23, 2019
Hypertension, Press, Healthy Lifestyle
Generic Medicines and a Healthy Diet for Heart Conditions
What do you need to do for a healthy heart? Take generic medicine for heart problems Uminom ng gamot sa high blood Start a [...]
-
March 13, 2020
Stroke
How to Prevent Heart Disease and Stroke
How can you prevent heart disease and stroke? Understanding The Risks Lower Your Blood Pressure Levels Watch Your Weight and Practice [...]